Quick overview of WebAuthn FIDO2 and CTAP
Overview of how FIDO2, CTAP, and WebAuthn work to create passkey experiences
There are a few concepts that help enable passkeys as a technology. It will be beneficial for you as an integrator of passkeys to be familiar with these terms.
WebAuthn
The Web Authentication API (WebAuthn) allows for the creation of a public-key based credentials for authenticating users. A server is able to invoke the API through a client application in order to perform two ceremonies: registration and authentication.
Registration allows a client application to work with a supporting authenticator to create a credential (passkey). This credential is sent to the backend application where it can be used to verify challenges signed by its corresponding private key during authentication ceremonies.
Registration requests are invoked using the navigator.credentials.create() method.
Authentication allows a client application to work with a supporting authenticator to sign a challenge, issued by the backend application. This verification is completed using the device’s private key. The signed challenge is returned to the backend application, where the public key captured during registration validates the challenge.
Authentication requests are invoked using the navigator.credentials.get() method.
Both the get() and create() API are supported by all of the major browsers, allowing web applications to seamlessly provide support across ecosystems.
CTAP
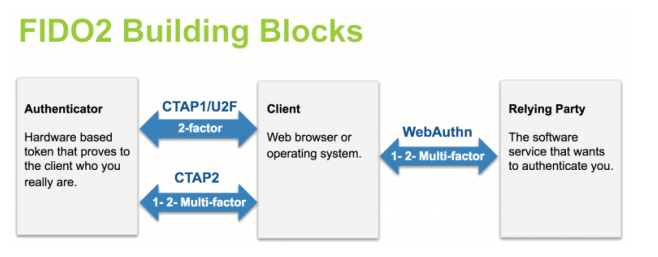
The client to authenticator protocol (CTAP) is a protocol that is used for communication between a client or platform, and an external authenticator. This is primarily used in scenarios where an authenticator like a security key is used to perform the WebAuthn operations.
FIDO2
FIDO2 is a standard that is built on the WebAuthn and CTAP standards, where they are able to work together to create strong authentication experiences.
Below is a diagram that provides an overview of how FIDO2 creates the concert of WebAuthn and CTAP to perform authentication ceremonies.

Now that we have an understanding of the foundational protocols that support passkeys, let’s dive into how they keep users secure.