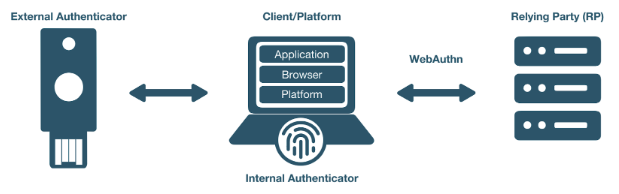
Integration Review Standard - FIDO
Applies to: FIDO2, WebAuthn, U2F, CTAP1, CTAP2
This provides guidance to developers on technical review standards for different integration protocols. Yubico conducts a technical review of integrations using YubiKeys to ensure that developers are meeting Yubico’s criteria for solid technical implementation of a YubiKey integration. This document outlines the review criteria.
Note: Not every section of this document is necessarily applicable to your integration.
The WebAuthn Readiness Checklist contains information similar to that in this current section, but set out as a series of points that developers need to address before submitting their apps. This section lists the criteria used to review apps that have been submitted.
FIDO Implementation

Supported Authentication Flows
Please indicate which authentication flows your app supports:
-
Single Factor Passwordless - Username and YubiKey
-
Second Factor - Username, password, and YubiKey
-
Multi-factor Authentication - YubiKey and PIN
-
Other (please describe):
Supported Platforms
What platforms does your solution support with YubiKeys? (Please check all that apply)
Mobile Support:
-
iOS (iPhone)
-
iOS/iPadOS (Tablet)
-
Android (Phone)
-
Android (Tablet)
-
Not Applicable
-
Other:
Laptop/Desktop Support:
-
Google Chrome
-
Chromium
-
Mozilla Firefox
-
Safari
-
Opera
-
Internet Explorer
-
Microsoft Edge
-
Not Applicable
-
Other:
Libraries
Yubico offers integration libraries such as Yubico java-webauthn-server, python-fido2, and other Yubico supported libraries found here.
-
What server-side libraries are being utilized?
-
What client-side libraries are being utilized? Please specify if they come built-in to browsers and platforms, or if they are custom built.
-
How are the client-side libraries being called: via NFC, USB or both?
-
How are the libraries being utilized?
Authenticator
-
Which YubiKeys were tested (Identify Your YubiKey)?
-
Please indicate which authenticators are supported:
-
CTAP1 (U2F)
-
CTAP2 (FIDO2)
-
-
The CTAP specifications provide support for extensions, if any are used please list them.
-
Transports supported:
-
USB
-
NFC
-
-
If user verification is being used for FIDO2 authentication, please describe the solution use case(s). A YubiKey supports user verification by entering a PIN.
Client
This section is applicable only if your solution implemented a client such as a desktop or mobile application. Please note that the Relying Party or Service section below is also applicable for Client implementations.
Token Binding
-
Is token binding in use (applicable for HTTPS communications)?
-
Yes
-
No
-
-
Utilizing browser or custom apps?
-
What is the behavior if a man-in-the-middle attack occurs?
Extensions
Both the WebAuthn and FIDO CTAP2 specifications provide support for a variety of extensions. The extensions below are the ones that are most pertinent to YubiKey implementation
-
Is AppID extension being used? (Part of the W3C WebAuthn specification)
-
Is the HMAC secret extension being used? (Part of FIDO CTAP2 specification.The HMAC Secret extension can be used for offline scenarios. See Microsoft’s post for more information.)
-
List any other extensions being used:
Relying Party or Service
This section is applicable only if the solution implemented a relying party or service.
User Verification
User verification (UV) is applicable only to FIDO2 WebAuthn implementations. Enabling user verification will cause the user to be prompted for a PIN to unlock the YubiKey prior to authenticating. We recommend explicitly enabling or disabling user verification for the solution’s specific use case to prevent unintended user interaction.
For second factor flows, to prevent a PIN prompt when using a YubiKey for authentication, we recommended setting UV to discouraged.
-
What values are set for UV for registration?
-
What values are set for UV for authentication?
Saving the Attestation Object
The Attestation Object is applicable only to CTAP2 and WebAuthn implementations.
Reference W3C standard.
After successful creation of a credential the attestation object should be saved. This enables future audits of credential creation.
Is the attestation object being saved?
Attestation for Authenticator Verification
Attestation is used to validate that the certificates being generated come from an authentic device. According to the WebAuthn specification, attestation is optional. However, we do recommend that developers review the importance of attestation and consider adding it to their YubiKey implementation. More information on attestation can be found here.
-
Is attestation being used?
-
Are custom attestation certificates required?
-
What metadata is required?
-
How is attestation being checked?
-
When and where is attestation being checked?
-
How are whitelisting and blacklisting being handled?
-
What is the behavior when rejecting devices based on whitelisting/blacklisting?
-
-
How are changes to attestation certificates being handled?
-
How is the metadata being stored, secured and backed up?
Extensions
The WebAuthn specifications provide support for a variety of extensions. The AppID extension (part of the W3C WebAuthn specification) is most pertinent to a YubiKey implementation.
-
Is the AppID extension being used?
-
Are any other WebAuthn extensions being used?
Restrictions
As a Relying Party, are you implementing any restrictions on the use of security keys such as checking the user agent?
Authenticator Lifecycle
The following YubiKey lifecycle items will be reviewed. Not all of these items will apply to every implementation. See the [Best Practices] section for more detailed information.
-
How many YubiKeys per account can be registered? Recommendation is at least two: primary key and a back-up; but ideally no upper limit.
-
Does an end-user have the ability to remove a registered YubiKey from their account?
-
If a YubiKey cannot be removed by the end-user, can a YubiKey be removed by an administrator? How does the end-user initiate this request?
-
Is there a method for account recovery when a user loses an authenticator? If so, what method is being used?
-
Does an end-user have the ability to name or rename registered YubiKeys?
Testing
-
What test process was used to test this integration - both client and server side - for example, unit testing, integration testing, PEN testing, or any other process?
-
What on-going tests will be employed to ensure the functionality does not break with future releases?
-
What test cases were covered as part of testing?
End User Support
Support plays a key role in quick resolution of issues and positive customer experience with YubiKeys and our technical partners.
-
Have you got a place to send customers for help? (e.g. web site URL, phone number, or anything else?)
-
Is there a contact to whom our support team can reach out if issues are discovered in the YubiKey implementation? If so, who?
-
If there are any troubleshooting steps that you can share with Yubico, what are they? (i.e., basic debugging, etc.)
-
Are there instructions on how to set up the YubiKey on your site? If so, can this documentation be shared with Yubico support?
Technical Review Tests
-
Register a YubiKey (only CTAP1/U2F enabled)
-
Register a YubiKey (only CTAP2/FIDO2 enabled)
-
Register a second YubiKey (only CTAP1/U2F enabled)
-
Register a second YubiKey (only CTAP2/FIDO2 enabled)
-
Authenticate using YubiKey (CTAP1/U2F enabled)
-
Authenticate using YubiKey (CTAP2/FIDO2 enabled)
-
Unregister/remove a YubiKey (self service or admin request)
-
Name or rename registered YubiKey
-
Prevent the same YubiKey from being registered again
-
For Second Factor use cases do not prompt for PIN when authenticating (CTAP2/FIDO2 only)
-
Login rejected with unregistered key
-
Correct terminology and Yubico/YubiKey branding.