Configuring the Primary YubiHSM 2 Device
The YubiHSM Setup program, which is part of the YubiHSM 2 toolset, is used to perform the initial configuration of the primary YubiHSM 2 device. This program configures the device with the requirements needed for deploying YubiHSM 2 to safely store the ADCS root CA key. Specifically, during the setup process the YubiHSM is configured so that:
-
The necessary key material is generated on the device:
-
One wrap key
-
One application authentication key
-
One audit key
-
The wrap key is split among a determined number of key custodians, and each share is recorded by each custodian
-
The authentication key and the audit key are exported under wrap to a file, located in the current working directory
To safeguard the integrity of the device, configuration must be performed in an air-gapped environment.
Summary of Configuration Steps
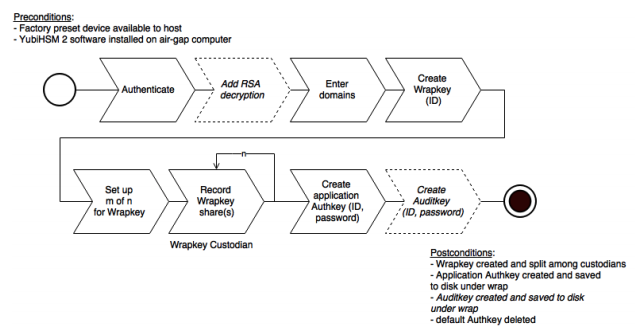
After you have inserted the primary device into the air-gapped system, the configuration steps are diagrammed in the following image, and listed below. They are described in detail in the next section, Configuration Procedure.

Configuration Steps
-
Set up communication between the YubiHSM 2 tools and the device.
-
Start the configuration process.
-
Authenticate to the YubiHSM device.
-
Specify if you need to add RSA decryption (not required if you are using YubiHSM 2 exclusively with ADCS).
-
Enter the domains you need the application authentication key and audit key to be available in.
-
Create the wrap key.
-
Split the wrap key into shares, and record the number of shares required to rejoin the wrap key.
-
Create the application authentication key, which is used to authenticate to the device by the KSP in Windows so the KSP can perform operations in YubiHSM 2.
-
Create the audit key, to access the internal audit log of the device which holds information about the last 62 operations performed and so you can reset the audit log.
Configuration Procedure
Step 1 Enable communication with the YubiHSM 2 device by ensuring that the YubiHSM Connector service (yhconsrv in Windows) is running on the system where the device is inserted. You can validate that the connector is running properly by typing the following URI into your browser: http://127.0.0.1:12345/connector/status. Output should be similar to:
status=OK serial=* version=1.0.0 pid=* address=127.0.0.1 port=12345
Step 2 In your command line application (where $ is the generic prompt used in this document; depending on your command line application, your prompt may be different), run YubiHSM Setup with the argument ksp. To do this, launch your command line application, navigate to the directory containing the YubiHSM Setup program, run yubihsm-setup ksp and press Enter.
|
Tip
|
The setup tool also has a help argument that you can call to learn more about its usage. |
Step 3 To start the YubiHSM Setup process, type the default authentication key password: password and press Enter. A message appears, confirming that the default authentication key was used and that you have successfully authenticated to the device: Using authentication key 0x0001. Object IDs are displayed in the YubiHSM Setup Tool using hexadecimal numbers, in this case the default authentication key has ID 1, or 0x0001 in hexadecimal.
Step 4 You are prompted to add RSA decryption capabilities. Do one of the following:
-
If you plan to use your YubiHSM 2 with ADCS exclusively, you will not need the RSA decryption capabilities, you will only need signing capabilities. Type
n. -
If you plan on using the same YubiHSM 2 device for purposes that do require decrypting RSA, type
y.
|
Tip
|
If you are unsure what selection to make, type |
Step 5 The next question to be answered is what domain(s) you need the application authentication key and audit key to be available in (the authentication and audit keys are generated after you create the wrap key). You will only need one domain for the purposes of completing this guide. Do the following:
-
Unless you have a requirement to assign more than one domain, type a single number between 1 to 16 and press Enter. In this guide, we assume that domain 1 was entered. Confirmation will look like the following:
got domains [ One ]
Step 6 In this step you will create a wrap key. The wrap key is very important as it allows you to export and import objects from and to the device. For example, you would export and import objects for backup purposes, as described in the section Backup Key Material. Do one of the following:
-
To manually assign a wrap key ID, type the number and press Enter. As object ID ‘1’ is already in use by the default application authentication key, we recommend you assign id ‘2’ to the wrap key. Type 2 and press Enter.
-
To allow the system to assign a wrap key ID automatically, type 0 and press Enter. A confirmation message is displayed:
-
Stored wrap key with ID 0x0002 on the device
-
Step 7 Now you will split the wrap key among a number of key custodians. For this example, we will assume that the wrap key is split into three shares, out of which at least two shares must be present in order to use the key. If there are not two key custodians present, the wrap key cannot be rejoined. When prompted, do the following:
-
Enter the number of shares. In this example, enter 3.
-
Enter the privacy threshold. In this example, enter 2.
When defined, the three wrap key custodians will each take their turn in front of the screen to record their respective share. A warning notice appears advising you that the shares are not stored anywhere.
|
Note
|
Be sure to record the shares and store them safely if you want to re-use the wrap key forthis device in the future. |
To start recording the key shares, press Enter.
The first custodian records his share and leaves the screen. The next one enters and repeats the key share recording for the second share, and so on. Each custodian confirms by pressing y that the share was recorded before handing over to the next. The screen buffer is cleared before each share is presented. Following is an example of a share presented on the screen:
2-1-WWmTQj5PHGJQ4H9Y2ouURm8m75QkDOeYzFzOX1VyMpAOeF3YKYZyAVdM0WY4GErclVuAC Have you recorded the key share? (y/n)
It is important to record the whole string presented, including the prefix (in this case) “2-1-” which indicates the number of shares determined to be required to rejoin (or the privacy threshold) and the number of the share itself out of the total number of shares being created.
|
Tip
|
For non-production purposes, such as in a lab scenario, it is not necessary to specify that the wrap key should be shared between key custodians but instead just use one solitary key. To do this, when configuring the device using YubiHSM Setup, indicate the number of shares to be 1 and the privacy threshold to also be 1. |
Step 8 The setup configuration continues by creating an application authentication key. This key is used to authenticate to the device by the Key Storage Provider (KSP) in Windows, allowing the KSP to perform operations in YubiHSM 2. Since object ID 1 and 2 are already in use by the default authentication key and the wrap key respectively, the example in this guide assumes that the application authentication key to be created next gets ID 3. Do one of the following:
-
To manually assign an application authentication key ID, type 3 and press Enter.
-
To instead allow the system to assign a wrap key ID automatically, type 0 and press Enter.
You also need to choose a password for the application authentication key. Be sure to store the password of the application authentication key that you will use in a way so that it cannot be compromised. You will need this information later to configure the KSP for use with ADCS. Enter the application authentication key password and press Enter. A confirmation message appears.
Stored application authentication key with ID 0x0003 on the device
Saved wrapped application authentication key to {path} 0x0003.yhw
The wrapped application authentication key (0x0003.yhw) has been saved to the same path as the location of the YubiHSM Setup program. Although encrypted using the wrap key, we recommend that you do not store keys under wrap on a network-accessible or otherwise potentially comprisable storage media. Leave the file where it was saved for now, as it will be used later to create a backup. You can remove the application authentication key afterwards.
Step 9 The final step of the YubiHSM 2 setup process is to decide whether to create an audit key. The audit key is used to access the internal audit log of the device which holds information about the last 62 operations performed. It is also used to reset the log if needed. Depending on your local requirements, you may not need to create an audit key. If you are unsure of your requirements, we suggest you create an audit key.
When prompted to create an audit key, type y. You are then prompted to assign a key ID to the audit key. Be sure to make a note of the ID you enter (for example, key ID 4). You are also prompted to enter the audit key password. Be sure to store this password as well, so that it cannot be compromised. Finally, the audit key will be exported under wrap to the current working directory. Using our example of key ID 4, the file will be named 0x0004.yhw.
Step 9 The setup tool finishes by letting you know that the default, factory-installed authentication key has been deleted.
Previous authentication key 0x0001 deleted All done
Finally, the YubiHSM Setup application exits.
Verifying the Setup
You can verify the results of the YubiHSM Setup program by using the YubiHSM Shell program, and logging in using the application authentication key (we used object ID 3 in this guide). To verify the YubiHSM Setup
-
In your command line application (where $ is the prompt), run YubiHSM Shell program. To do this, if you haven’t already, launch your command line application and navigate to the directory containing the YubiHSM Shell program. Then run the following command and press Enter.
$ yubihsm-shell -
To connect to the YubiHSM, at the yubihsm prompt, type connect and press Enter. A message verifying that you have a successful connection is displayed.
-
To open a session with the YubiHSM 2, type session open 3 and press Enter.
-
Type in the password for the application authentication key. You will receive a confirmation message that the session has been set up successfully.
-
You now have an administrative connection to the YubiHSM 2 and can list the objects available. To list the objects, type list objects 0 and press Enter. Your results should be similar to the following:
Found 3 object(s) id: 0x0002, type: wrapkey, sequence: 0 id: 0x0003, type: authkey, sequence: 0 id: 0x0004, type: authkey, sequence: 0
As you can see by looking at their IDs, these objects correspond to the wrap key, the application authentication key and the audit key that were just created.
To obtain more information about any one of the objects, for example, the application authentication key (object ID 3), including its capabilities, type the following command and press Enter:
yubihsm> get objectinfo 0 3 authentication-key
The response you receive should look similar to the following:
id: 0x0003, type: authkey, algorithm: yubico-aes-auth, label: "Application auth key", length: 40, domains: 1, sequence: 0, origin: imported, capabilities: asymmetric_gen:asymmetric_sign_pkcs:asymmetric_sign_pss:export_wrapped:import _wrapped:export_under_wrap, delegated_capabilities: asymmetric_gen:asymmetric_sign_pkcs:asymmetric_sign_pss:export_under_wrap
This indicates that YubiHSM 2 as it has now been configured will later on allow the KSP to leverage the device to:
-
Generate asymmetric objects
-
Compute signatures using RSA-PKCS1v1.5
-
Compute signatures using RSA-PSS
-
Export other objects under wrap
-
Import wrapped objects
-
Mark an object as exportable under wrap
In addition, this object (the application authentication key, object ID 3) also has so-called delegated capabilities. Delegated capabilities define the set of capabilities that can be set or "bestowed" onto other objects that are created by it.
To exit, type quit.